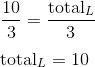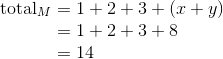This page is part of my unofficial solutions manual to the GRE Paper Practice Book (2e), a free resource available on the ETS website. They publish the questions; I explain the answers. If you haven’t worked through the Practice Book, give Section 5 a shot before reading this!
5.14: An Average Problem
The trick to this problem is recognizing that we can’t solve for x and y separately; there just isn’t enough information. Instead, we have to solve for the sum of x and y and use that to figure out what’s going on in list M.
To find an average, we sum all of the values in a data set, then divide by the number of values in that set:
We can use this formula to find any of these three pieces of information, provided that we have the other two:
- If we know the total and the number of values, we can find the average.
- If we know the average and the total, we can find the number of values.
- If we know the average and the number of values, we can find the total.
That last application is what we need here. For list L, we know the average (10/3) and the number of values (3), so we can solve for the total:
Once we know the total of list L, we can determine the value of x + y:
That, in turn gives us enough information to find the total of list M:
We already know the number of values in M (5), so we can now solve for the average:
In this case, no further simplification was necessary. But remember: on an NE problem, you don’t need to convert your answer to lowest terms unless explicitly instructed to do so. If your answer is equal to the right answer, it is the right answer.
Math Review Reference
For more on this topic, see the following section of the GRE Math Review:
- 4.2: Numerical Methods for Describing Data (pp. 68-69)