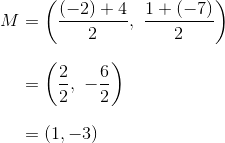This page is part of my unofficial solutions manual to the GRE Paper Practice Book (2e), a free resource available on the ETS website. They publish the questions; I explain the answers. If you haven’t worked through the Practice Book, give Section 6 a shot before reading this!
6.12: The Midpoint Formula
The GRE Math Review doesn’t actually discuss the midpoint formula, but it’s a fundamental coordinate-geometry fact and ought to be committed to memory. You may not need it to get a problem right on the GRE, but knowing it will certainly save you some time if you encounter a question like 6.12.
Here’s the standard form of the formula:
![]()
And here’s a prose translation:
To find the midpoint M of two points on an xy-plane, we take the averages, respectively, of the x– and y– coordinates. The x-coordinate of M is the average of the x-coordinates; the y-coordinate of M is the average of the y-coordinates.
To find the midpoint of R and S, let R be point 1 and S be point 2. Then:
which corresponds to answer choice (C).
Note that this is yet another coordinate-geometry problem we solved without diagramming. I probably seem like I’m harping on this point, but I’ve had more than one student approach this problem by methodically sketching out a pair of xy-axes, then locating R and S on the coordinate plane. This kind of detail is fine if you’re submitting homework for a persnickety TA, but it’s counterproductive on the GRE, where time is of the essence.
Math Review Reference
For more on this topic, see the following section of the GRE Math Review:
- 2.8: Coordinate Geometry (pp. 30-32)